|
|
 GLACIORISK EUROPEAN PROJECT
GLACIORISK EUROPEAN PROJECT
 |
|
France (CEMAGREF,
ETNA,
ONF-RTM,
LGGE-CNRS), Italy (CNR-IRPI,
SMS/Nimbus), Norway (UOSLO,
NVE),
Iceland (UI
(IS)), Austria (DGGS),
Switzerland (VAW-ETHZ) |
|
WELCOME TO GRIDABASE, GLACIER RISKS DATA BASE :
MAIN MENU
Gridabase
was implemented by
SMS/Nimbus
|
|
|
|
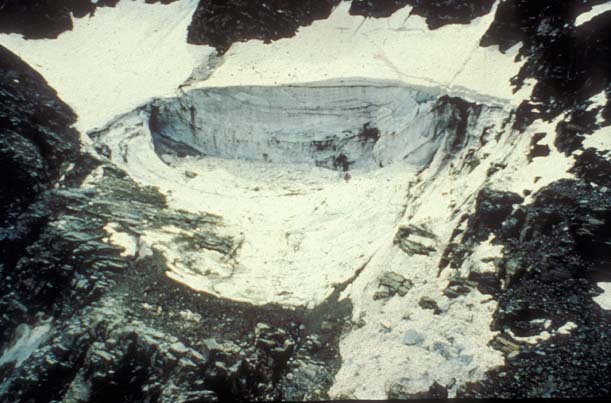
GLACIER "COOLIDGE"
Risk type: ice avalanches
Glacier list |
Statistics
|
| Type: |
Niche glacier |
| Country: |
Italy |
| Region: |
Piemonte |
| Massif/Ice Cap: |
Monviso |
| Municipality: |
Crissolo-CN |
| Municipality code: |
|
| Location: |
|
|
|
| Latitude (°, cent): |
4 N |
|
| Longitude (°, cent): |
7,09367 E |
| Surface (km2): |
0,15 |
| Lenght (km): |
1,3 |
| Width (km): |
|
| Min. altitude (m): |
2490 |
| Max. altitude (m): |
3800 |
| Orientation (°) |
360 |
| Slope (°) |
50 |
|
|
EVENT: Date
6/7/1989
- Date quality: |
 |
| Type: |
Ice avalanches |
 |
|
| Description |
On 6th July 1989, at 10:45 P.M., 2/3 of Superiore di Coolidge glacier (northern face of Monviso) collapsed. The detach occurred at 3195 m, in correspondence of a rectilinear crevasse in the upper part of glacier, involving all the glacial mass till the bedrock (volume of about 200.000 m3). The ice mass fell along the "canalone Coolidge". The impact onto ghiacciaio Inferiore di Coolidge was clearly noticed in the town of Crissolo (upper Po valley), and recorded by seismograph in Stroppo (Maira valley), 20 km southward. The phoenomenon developped in ice-avalanche mixed with debris charged along the path, reaching Lago Chiaretto (2265 m), that was partly filled, and going up again along the opposite slope for 50 m. The ice-mass covered a path of about 1200 m in less than a minute, and a total different of altitude of 950 m.
Climatic and morphological elements caused the collapse: a warm period and rain on the glacier, with the presence of liquid water at the bedrock, probably favoured the sliding of the ice.
|
|
Effects: |
Accumulation of ice and debris on Inferiore di Coolidge glacier and into Lago Chiaretto (2265 m), and overflow of the ice-avalanche for 50 m of level on the opposite slope.
Debris and ice accumulation spreaded in a 250.000 m2 surface.
The avalanche involved the "bivacco Villata" with a violent air movement, but two mountaineers that lodged inside remained unhurt. |
| Deaths(#) |
0 |
|
|
|
Injuried (#) |
0 |
| Note |
The crevass in the upper part of glacier was already observed in 1986, but the glacier morphology didn't suggest such a quick evolution. |
|
DAMAGES |
 |
| Type: |
Trail |
Description: |
|
|
BIBLIOGRAPHY |
 |
|
Dutto F., Godone F., Mortara G., 1991 - L'écroulement du glacier supérieur de Coolidge (Paroi nord du Mont Viso. Alpes occidentales) Rev. Géographie Alpine, n. 2 |
|
Mortara G. & Dutto F., 1990 - Un episodio parossistico nell'evoluzione dei ghiacciai del gruppo del Monviso: il crollo del Ghiacciaio Superiore di Coolidge Geografia fisica e dinamica quaternaria. Vol 13 (2), 1990, p. 187. |
|
|